Outcome:
At the end of this Student will be familiar with the lpc17xx GPIO and SFR registers and how to access them and configure them.
General Purpose Input Output is what let’s microcontroller be something more than a weak auxiliary processor. With GPIOs MCU can interact with the physical world, connecting up other devices and turning microcontroller into something useful.
LPC1768 Memory Map
As it is 32-bit architecture it can access 2^32 locations(4GB).
This 4Gb of addressable locations are divided into ROM, RAM, GPIO, AHB Peripherals as shown in the below image.
In LPC1768 the GPIO registers are mapped to memory location 0x2009 C000 - 0x2009 FFFF.
Register Configuration
LPC1768 has its GPIOs divided into five ports PORT0 - PORT4, although many of them are not physically 32bit wide.
The Below registers will be used for Configuring and using the GPIOs registers for sending and receiving the Digital signals.
Lets consider 100 pin LPC1768 as an example.
Pins on LPC1768 are divided into 5 groups (PORTs) starting from 0 to 4.
Pin naming convention: Px.y
Ex: P0.0 (group 0, pin 0) or (port 0, pin 0).
Each pin has 4 operating modes:
GPIO(default), 1st alternate function, 2nd alternate function, 3rd alternate function.
Details about the configuration of GPIO port pins.
1. Pin Function Setting
The LPC_PINCON register controls the operating mode of these pins.
Bit Value
|
Function
|
00
|
GPIO Function
|
01
|
1st alternate function
|
10
|
2nd alternate function
|
11
|
3rd alternate function
|
Example:
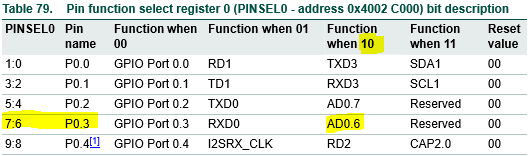
To set pin 0.3 as GPIO (set corresponding bit to 00)
LPC_PINCON –> PINSEL0 &= ~ ((1<<7) | (1<<6));
To set pin 0.3 as ADC channel 0.6 (2nd alternate function, set corresponding bit to 10)
LPC_PINCON –> PINSEL0 &= ((1<<7) | (0<<6)); // you may omit (0<<6)
For reference follow [Page No: 108, Table: 79]
2. Pin Direction Setting
Register LPC_GPIOn –> FIODIR [31:0] control the pin input/output, where ‘n’ stands for pin group (0-4). To set a pin as output, set the corresponding bit to ‘1’. To set a pin as input, set the corresponding bit to ‘0’, by default, all pins are set as input (all bits are 0).
Example:
To set 0.3 as output
LPC_GPIO –> FIODIR |= (1<<3);
3. Pin is Set as Output
A pin digital high/low setting
LPC_GPIOn –> FIOSET is used to turn a pin to HIGH. Register LPC_GPIOn –> FIOCLR is used to turn a pin to low. To turn a pin to digital ‘1’ (high), set the corresponding bit of LPC_GPIOn –> FIOSET to 1. To turn a pin to digital ‘0’ (low), set the corresponding bit of LPC_GPIOn –> FIOCLR to 1.
Example
Turn Pin 0.3 to high
LPC_GPIO0 –> FIOSET |= (1<<3);
If we set LPC_GPIOn –> FIOSET bit to ‘0’ there is no effect.
Turn Pin 0.3 to low
LPC_GPIO0 –> FIOCLR |= (1<<3);
If we set LPC_GPIOn –> FIOCLR bit to ‘0’ there is no effect.
4. Pin is Set to Input
Read a Pin Value
Register LPC_GPIOn –> FIOPIN stores the current pin state. The corresponding bit is ‘1’ indicates that the pin is driven high.
Example
To read current state of Pin 0.3
Value = ((LPC_GPIO0 –> FIOPIN & (1<<3)) >> 3);
Note: write 1/0 to corresponding bit in LPC_GPIOn –> FIOPIN can change the output of the pin to 1/0 but it is not recommended. We should use LPC_GPIOn –> FIOSET and GPIOn –> FIOCLR instead.
- Pin Internal Pull up Setting
Register LPC_PINCON –> PINMODEn is used to set up a pin internal pull-up.
LPC_PINCON –> PINMODE0 [1:0] control P0.0 internal pull-up
…..
LPC_PINCON –> PINMODE0 [31:30] control P0.15 internal pull-up,
Please see LPC_PINCON –> PINSELn for the full list [Page No: 114].
Bit Value
|
Pin Mode
|
00
|
On chip pull-up resistor enabled
|
01
|
Repeater Mode
|
10
|
Tri-State mode, (neither pull-up nor pull-down)
|
11
|
On chip pull-down resistor enabled
|
- Example:
By default all pins which are set as input has internal pull-up on (00).
- To disable internal pull-up on pin 0.3
LPC_PINCON –> PINMOD0 |= (1<<7);

or paste below link
http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.dui0489c/Cacigaci.html